We have talked a lot about furnace failures, repairs, and replacement in our blog and we want to go more in depth about furnace heat exchanger design, how they work, and why they fail.
The Most Dangerous Furnace
*This 75k BTU furnace was installed in a crawlspace and vented to the roof using 3″ “B” vent. We solved this issue by installing a high efficiency furnace using pvc vent out the side of the home.
What it does…
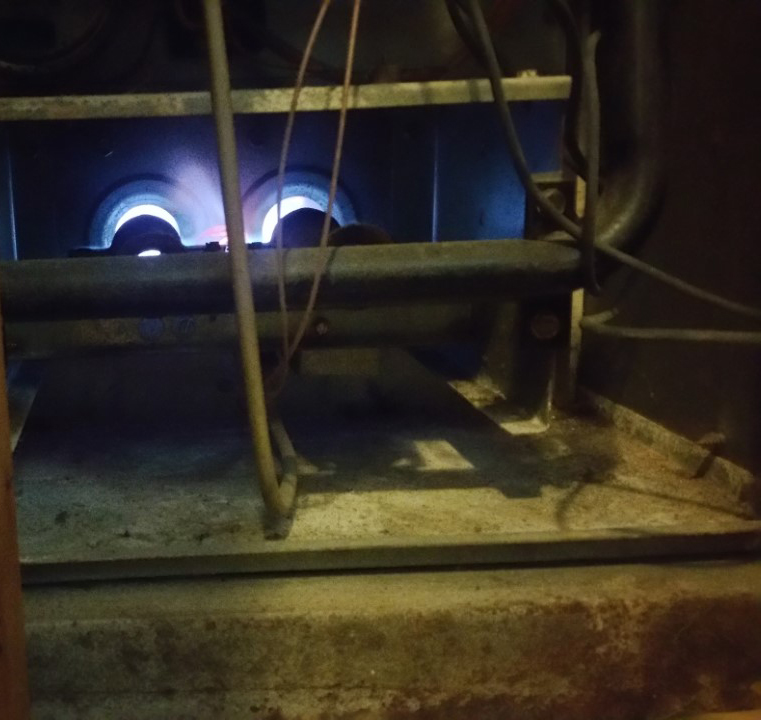
A furnace’s heat exchanger uses some type of fuel/air mix to burn inside of it, creating heat and getting very hot. Your blower motor (aka your ‘fan’) then blows air over this heat exchanger. The air passes over absorbing heat off the surface conditioning it to warm air. The warm air is then distributed throughout the duct work into the conditioned space.
Sign’s & Symptoms of Failure
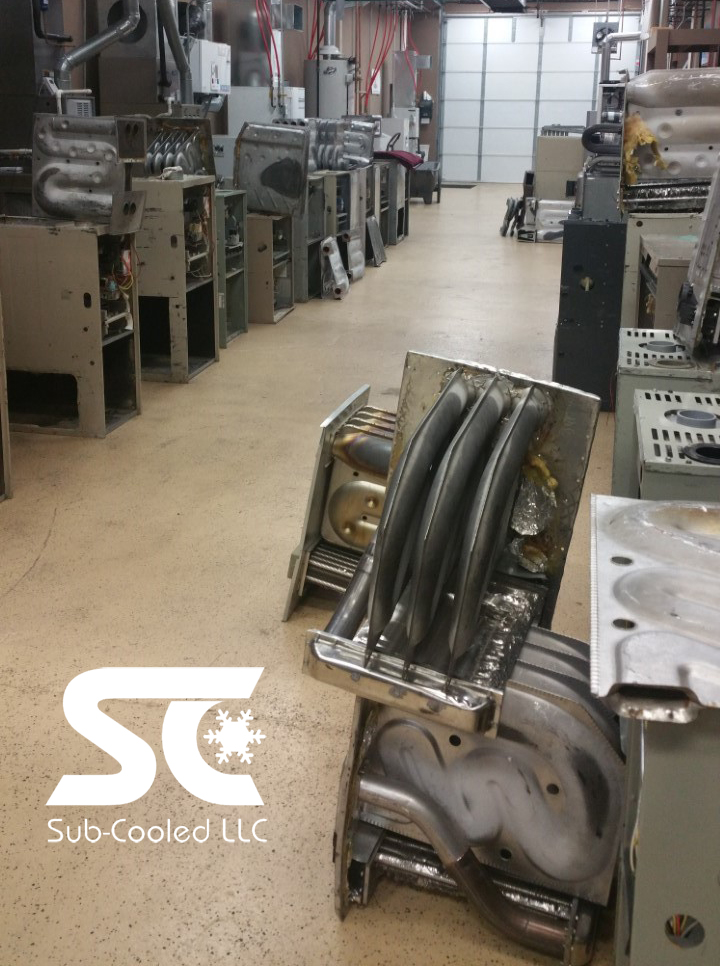
All pictures shown below are findings from our field service technicians
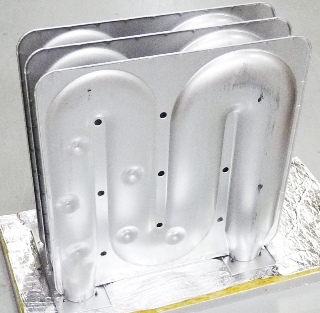
Common Forced Air Furnace Heat Exchanger Designs
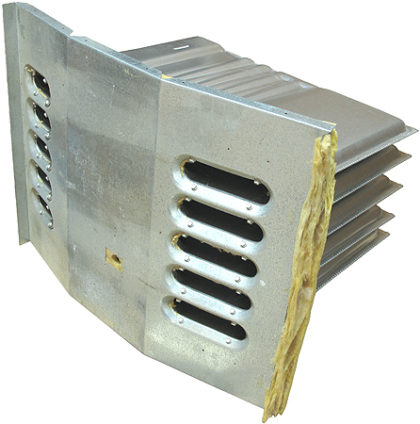


What Causes a Furnace Heat Exchanger To Fail?
*Testing a natural draft furnace heat exchanger cell.
-
- Furnace BTU over sized for the house (will cause excessive corrosion & premature failure)
-
- Not enough return air going through the furnace. (causes metal stress, cracks, and opens welds or seams)
-
- One-inch pleated furnace filter restricting air flow across the furnace heat exchanger.
-
- Furnace filters not change often enough which will restrict air flow across the heat exchanger.
-
- The gases from house hold chemicals such as bleach, fabric softener, hair spray, ect.
-
- Furnaces that run during home construction or remodeling process’s. (out-gassing from building materials)
-
- Water leaks from a humidifier that is not maintained often enough.
-
- Water leaks from the air conditioning coil, there are a number of possibilities that cause this.
-
- Manufacturing process that is not checked for accuracy often enough.
- Poor manufacturing design.
Thermal Fatigue – Crack Initiation
Thermal expansion and contraction caused by alternate heating and cooling creates repetitive pulling and is a common cause for crack initiation. Cracks generally form at sharp corners, welds,and backside of the heat exchanger, due to restrictive air flow.
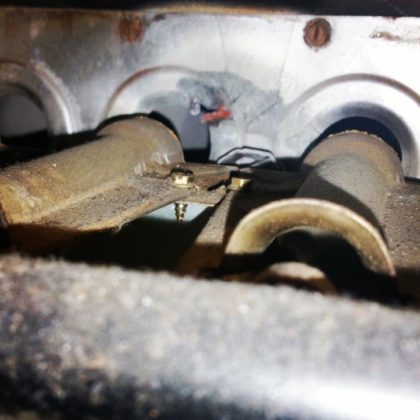






Furnaces fail for a number of reasons. Improper installations, lack of sufficient combustion air, a deficiency in return air, over firing of burners, improper venting, humidity, dirty air filter, old age, ect…
In concluding, we would like to add that when condemning the equipment and investigating these types of failures there are several factors. We have found installation issues such as duct design, filter selection and filter maintenance, condition of blower wheel or blower tap selection, as well as firing rate to be factors which shorten heat exchanger lifespan.
Customers must trust their lives to the experience, knowledge, and thoroughness of the service provider they choose. While that statement may seem a bit dramatic, it is nonetheless true. The only way to really stop premature failure and ensure the reliability and safety of your equipment is annual maintenance. Our maintenance program starts at $139.00 a year. For more information, call today! 219-476-3776